What is Ion Exchange Resin?
Ion exchange materials are essential in various applications, including water treatment, chemical separation, and purification processes. These materials consist of insoluble substances that contain loosely held ions capable of being exchanged with other ions in solution. The exchange occurs without altering the physical structure of the ion exchange material.
Ion exchangers can be categorized as cation exchangers or anion exchangers, depending on their ability to exchange positively or negatively charged ions, respectively. They are typically insoluble acids or bases that have salts with limited solubility. This unique property allows them to selectively exchange ions based on their charge.
Not only are ion exchange materials artificially synthesized, but they also occur naturally in various substances such as proteins, cellulose, living cells, and soil particles. These natural substances exhibit ion exchange properties that are vital to their functions in nature. For example, ion exchange processes in soil particles play a crucial role in nutrient uptake by plants.
Ion Exchange takes care of the chemical constituents in water and aims at correcting or reducing dissolved impurities in water. It is essentially a purification stage in which the quantum of impurities are lowered to a few parts per million and often to the parts per billion level.
The process of Ion Exchange is used to :
Soften a source of hard water
Dealkalise water with a high alkalinity
Demineralize water completely
What is Ion Exchange Resin made up of?
It is the synthetic organic substance with solid matrix situated with exchange sites. To Specify any Resin, we need below four information :
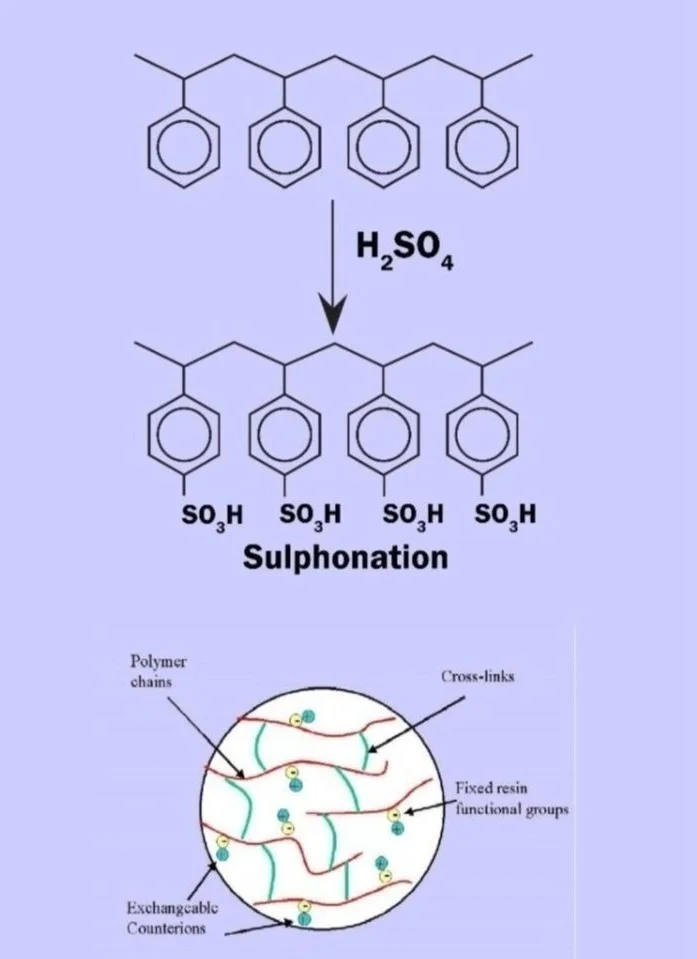
Matrix: Matrix is a solid backbone on which functional groups are attached. Ex. Styrinic, Acrylic, Phenol formaldehyde.
Functional Groups: These are the chemical groups attached to matrix. Ex. Sulphonic, Quaternary ammonium, Carboxylic etc.
Ionic form: Ionic form is the exchangeable portion in the resin chemical structure. Ex. H+, Na+, Cl-, OH-
Type / Structure : Iso Porous, Macro porous, Gel it stand out.
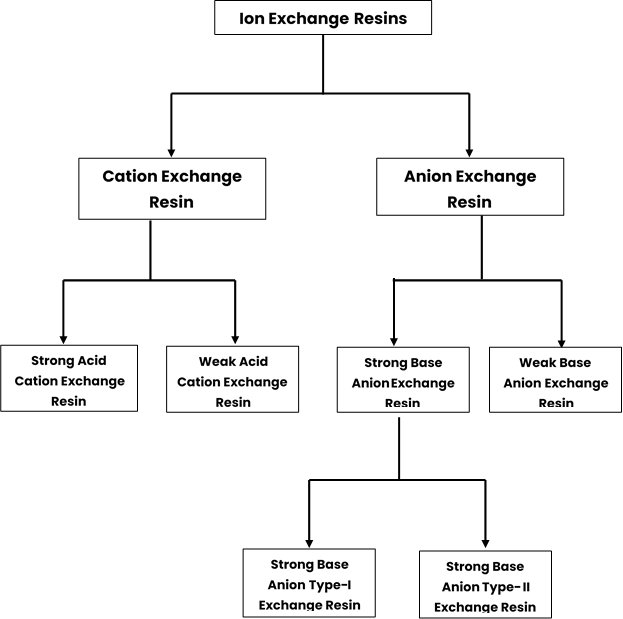
Different types of Ion Exchange Resin
Classification of Ion exchange resins is given below:
How does Ion exchange Resins make hard water soft?
Hardness in water:
Hard water is characterized by high levels of minerals, particularly calcium and magnesium ions. These ions can cause issues in water pipes by precipitating out and forming deposits. They can also interfere with the lathering ability of soap, leaving behind a scummy residue. Hard water has a distinct metallic taste and can leave a dry feeling on the skin. It is responsible for the formation of scum rings in bathtubs.
Types of Hardness:
Hardness of water can be temporary or permanent. Temporary hardness can be removed by boiling the water, while permanent hardness requires treatment with substances like washing soda or Calgon.
The permanent hardness of water, which is caused by salts of calcium and magnesium, can be softened by using a measured quantity of washing soda. Washing soda reacts with soluble salts like calcium sulfate and magnesium sulfate to form insoluble carbonates. These insoluble carbonates can then be filtered out, effectively removing the permanent hardness of water.
Softening Process:
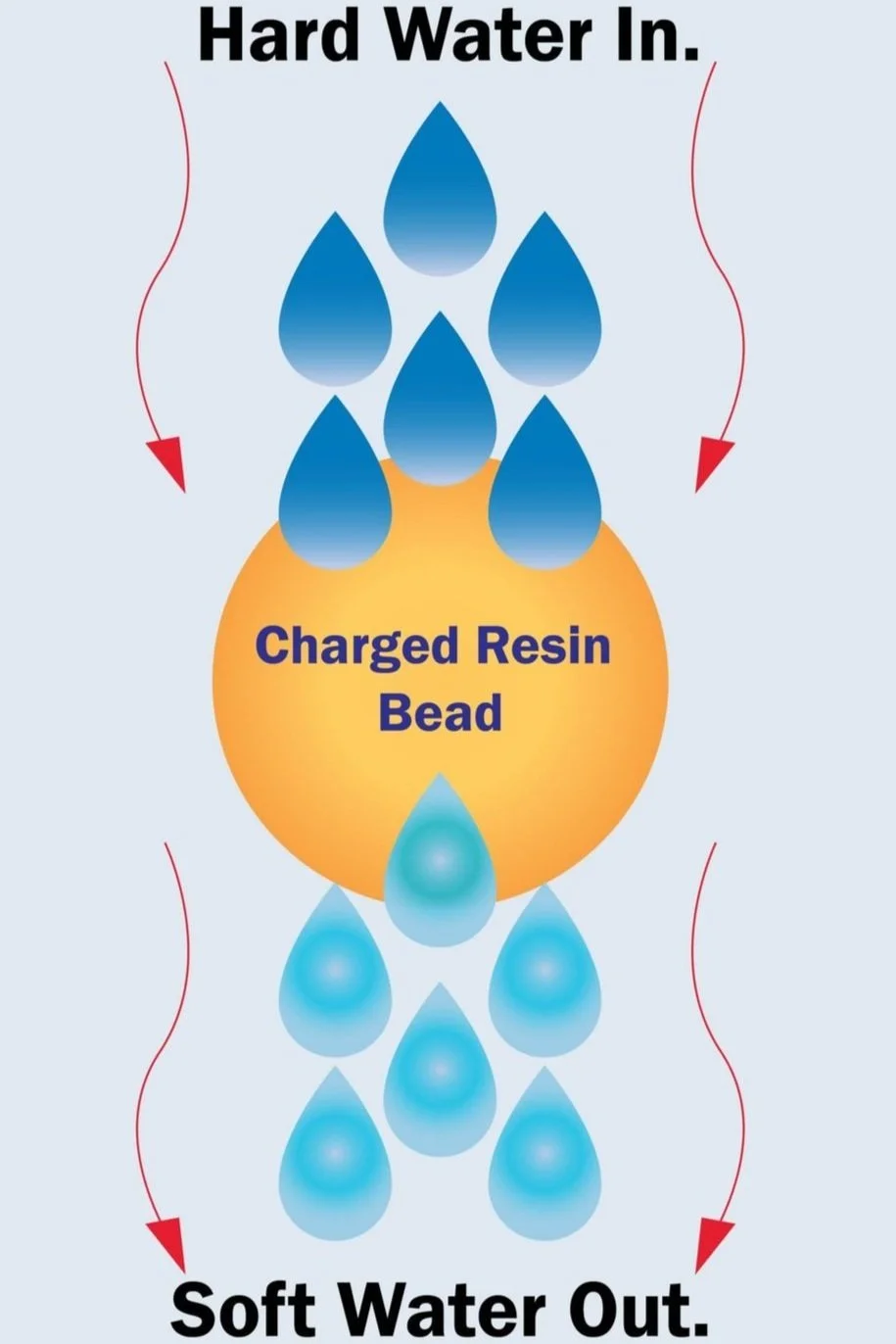
In this process hard water is converted into soft water. Thus the calcium and magnesium ions responsible for the hardness in the incoming water are replaced by the less harmful and acceptable sodium ion thereby making the water soft. Usually, Ion exchange resin of sodium form (Na+) is used in Water Softening process.
Water softening resin works through a process called ion exchange. When hard water containing dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium flows through the resin bed, the positively charged ions of these minerals are attracted to and captured by the negatively charged sites on the resin beads.
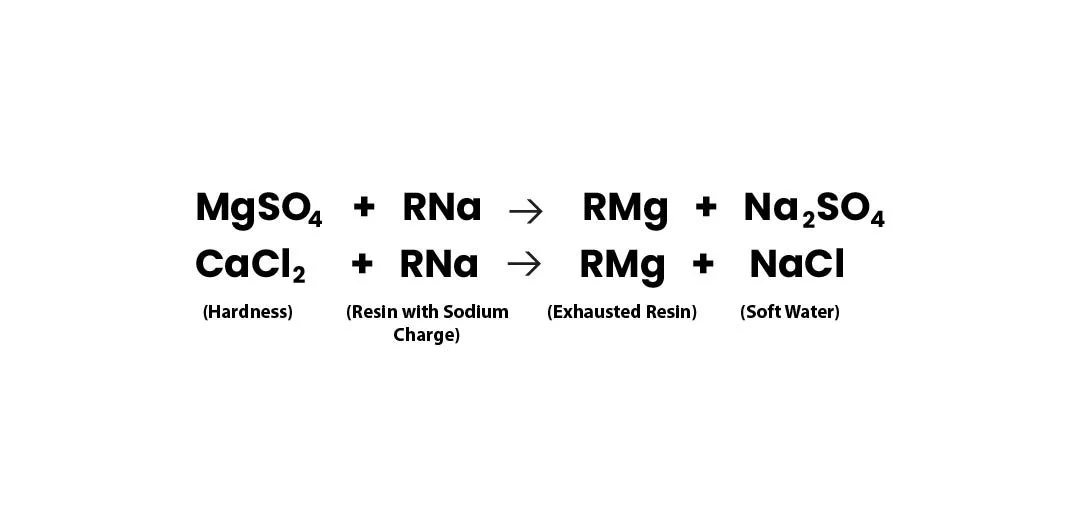
Softening Reaction
Once the resin gets saturated with Ca++ & Mg++ ions, it is regenerated with NaCl to again make it ready for softening.
During regeneration, the hardness ions are exchanged with the sodium ions from the brine solution (NaCl Solution), restoring the resin's capacity for further water softening.
Regeneration Reactions
Explore Doshion's industrial water treatment resins for process transformation. Visit Doshion's Industrial Water Treatment Resins page : https://www.doshionpoly.com/ion-exchange-resin